Tác giả :
The MET programme aims to train good practitioners in an emerging field that combines mechanical engineering, electrical engineering and computer science.
Programme Objectives
The MET program is to prepare students to:
1/ Apply general knowledge, fundamental knowledge and specialized knowledge to work effectively and implement lifelong learning in the profession.
2/ Analyze thoroughly the production system with problem solving skill and professional skills.
3/ Communicate effectively in the profesional enviroment, leadership and team work situations.
4/ Conceive, design, implement, operate and maintain Mechatronics systems.
5/ Specify requirements of industry to fulfill the needs of customers.
Job Opportunities
After graduation, students could work in mechanical engineering, electrical and electronic engineering, chemical engineering, food processing or technical services companies and factories in the role of engineers or operation managers.
The expected learning outcomes:
After successful completion of the programme, students will be able to:
- ELO 1: Use general knowledge of mathematics and science.
- ELO 2: Apply the principles of fundamental engineering knowledge.
- ELO 3: Apply advanced engineering knowledge in the professional areas of mechanical, electrical and electronic, and automation engineering.
- ELO 4: Identify, formulate, analyze and solve Mechatronics problems.
- ELO 5: Conduct investigations and experiments about Mechatronics engineering problems.
- ELO 6: Demonstrate professional skills that contribute to successful engineering practice.
- ELO 7: Lead and work effectively in individual and group-oriented settings.
- ELO 8: Communicate effectively in different forms: written, multimedia, graphical, and oral communication.
- ELO 9: Communicate effectively in English.
- ELO 10: Recognize the importance of the role and responsibility of engineers and the social context in the practice of engineering.
- ELO 11: Appreciate different enterprise cultures, demonstrate professional behavior and work successfully in organizations.
- ELO 12: Participate in lifelong learning
- ELO 13: Conceive and develop requirements and functions of components in Mechatronics systems.
- ELO 14: Design components for Mechatronics systems.
- ELO 15: Implement processes of hardware and software for Mechatronics systems.
- ELO 16: Operate the automation systems and manage the operation proces.
The relationships between knowledge, skills and ELOs
|
Group of ELOs
|
ELOs
|
|
General knowledge
|
- § ELO 1: Use general knowledge of mathematics and science.
|
|
Technological knowledge
|
- § ELO 2: Apply the principles of fundamental engineering knowledge.
- § ELO 3: Apply advanced engineering knowledge in the professional areas of mechanical, electrical and electronic, and automation engineering.
- § ELO 4: Identify, formulate, analyze and solve Mechatronics problems.
|
|
Generic skills
|
- § ELO 7: Lead and work effectively in individual and group-oriented settings.
- § ELO 8: Communicate effectively in different forms: written, multimedia, graphical, and oral communication.
- § ELO 9: Communicate effectively in English.
|
|
Attitude and awareness
|
- § ELO 10: Recognize the importance of the role and responsibility of engineers and the social context in the practice of engineering.
- § ELO 11: Appreciate different enterprise cultures, demonstrate professional behavior and work successfully in organizations.
- § ELO 12: Participate in lifelong learning.
|
|
Professional skills
|
- § ELO 5: Conduct investigations and experiments about Mechatronics engineering problems.
- § ELO 6: Demonstrate professional skills that contribute to successful engineering practice.
- § ELO 13: Conceive and develop requirements and functions of components in Mechatronics systems.
- § ELO 14: Design components for Mechatronics systems.
- § ELO 15: Implement processes of hardware and software for Mechatronics systems.
- § ELO 16: Operate the automation systems and manage the operation process.
|
|
All ELOs of the programme fully satisfy the requirements of the stakeholders and are highly evaluated. Matrix of programme objectives versus expected learning outcomes is illustrated in table
Matrix programme objectives vs. expected learning outcomes
|
Programme Objectives
|
Expected Learning Outcomes
|
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
9
|
10
|
11
|
12
|
13
|
14
|
15
|
16
|
|
1
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2
|
|
|
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
5
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
|
|
To transfer the ELOs into the programme, FME analyzed the requirements of ELOs and identified the knowledge (general and technical knowledge), skills (generic and professional skills) and attitudes-awareness (ethics and life-long learning) that should be educated to students along the programme .
According to the ELOs, the course learning outcomes, teaching content, teaching activities and assessment methods of all courses in the MET programme were reviewed and revised to ensure completeness and consistency. Each course has to contribute to the attainment of certain ELOs for students. The integration of overlapping courses, elimination of courses with less contributions or adding new courses were also implemented. The programme is reviewed annually and then revised if necessary according to the policy of the FME faculty for reviewing and updating the curriculum. The ELOs for soft skills and attitudes are also transferred to the programme via extracurricular activities such as seminars, union activities, social activities. All the curricular and extracurricular activities are hold throughout the programme and collaborate with each other to give students opportunities to experience various learning environments (in class, factory, society, etc). This assures a complete attainment of all ELOs in the programme.
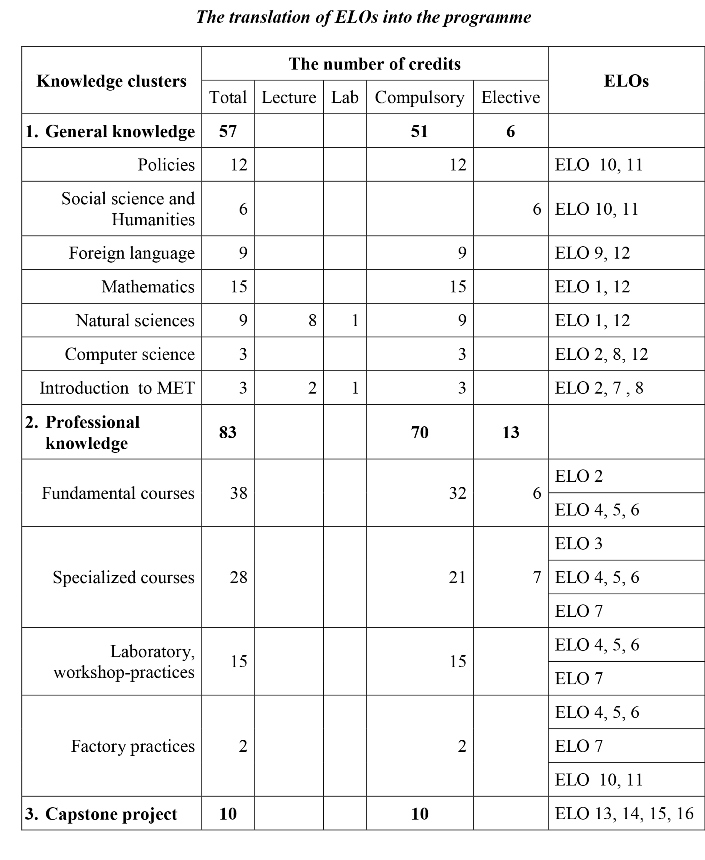
Programme 132 credits (from 2018): Mau 1_Nganh CNKT Co Dien Tu.pdf
|
Full Name:
|
*
|
|
| Email:
|
*
|
|
|
Title:
|
*
|
|
|
Captcha:
|
(*)
|
RadEditor - HTML WYSIWYG Editor. MS Word-like content editing experience thanks to a rich set of formatting tools, dropdowns, dialogs, system modules and built-in spell-check.
| RadEditor's components - toolbar, content area, modes and modules |
| | | |
| Toolbar's wrapper | | | | | |
| Content area wrapper | |
| RadEditor's bottom area: Design, Html and Preview modes, Statistics module and resize handle. |
It contains RadEditor's Modes/views (HTML, Design and Preview), Statistics and Resizer
| Editor Mode buttons | Statistics module | Editor resizer |
| |
|
|
| RadEditor's Modules - special tools used to provide extra information such as Tag Inspector, Real Time HTML Viewer, Tag Properties and other. | |
| | | |
*
|
|
|
| |